Sweetgum
Liquidambar styraciflua L.
Description
Sweetgum, or redgum, is a deciduous tree in the sweetgum family (Altingiaceae). It can reach heights of 50 to 80 feet (maximum 150 feet), and may have a deep or shallow rotted depending upon the drainage¹. Leaves are alternate on the stem and has a distinctive 5-pointed star shaped leaf with serrated margins and palmate venation and are 4 to 7 inches across7 . In the fall the leaves turn crimson, red, orange or yellow7 . Corky ridges may form distinctive wings on either side of the stem. Its produces male and female flowers on the same tree (monecious). It is wind pollinated. The female flowers are in heads that produce a round, prickly ball (gumballs) when mature¹. It is considered to be shade intolerant¹.

Bark of sweetgum. @ J. Brighton* 2013, Maryland Biodiversity Project8

Corky ridges on twig of sweetgum. @ B. Hubick* 2016, Maryland Biodiversity Project8

Leaves and male flowers of sweetgum. @ Z. Akulova (CC BY-NC-SA 3.0), CalPhoto³
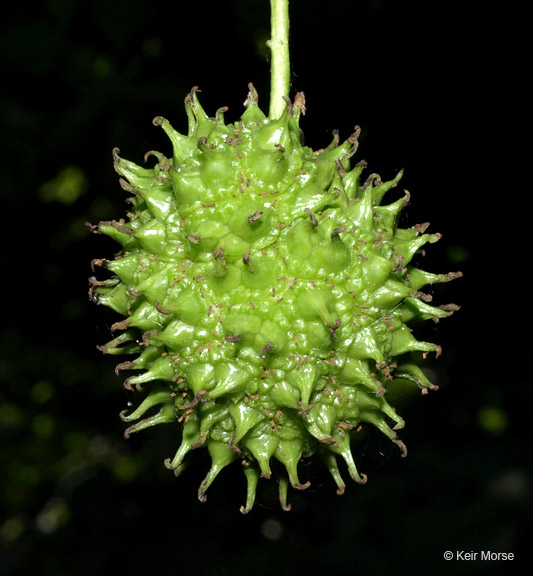

Fruit of sweetgum. @ K. Morse, 2016 (CC BY-NC-SA 3.0), CalPhoto6
Distribution
Sweetgum ranges from Connecticut to Florida and west to Texas and Arkansas and south into Mexico and Central America 7 . It is predominately a bottomland species, but can attain high frequency in the Piedmont of North Carolina and Georgia. In Maryland it is largely restricted to the coastal plain². Sweetgum is planted worldwide as a street tree.
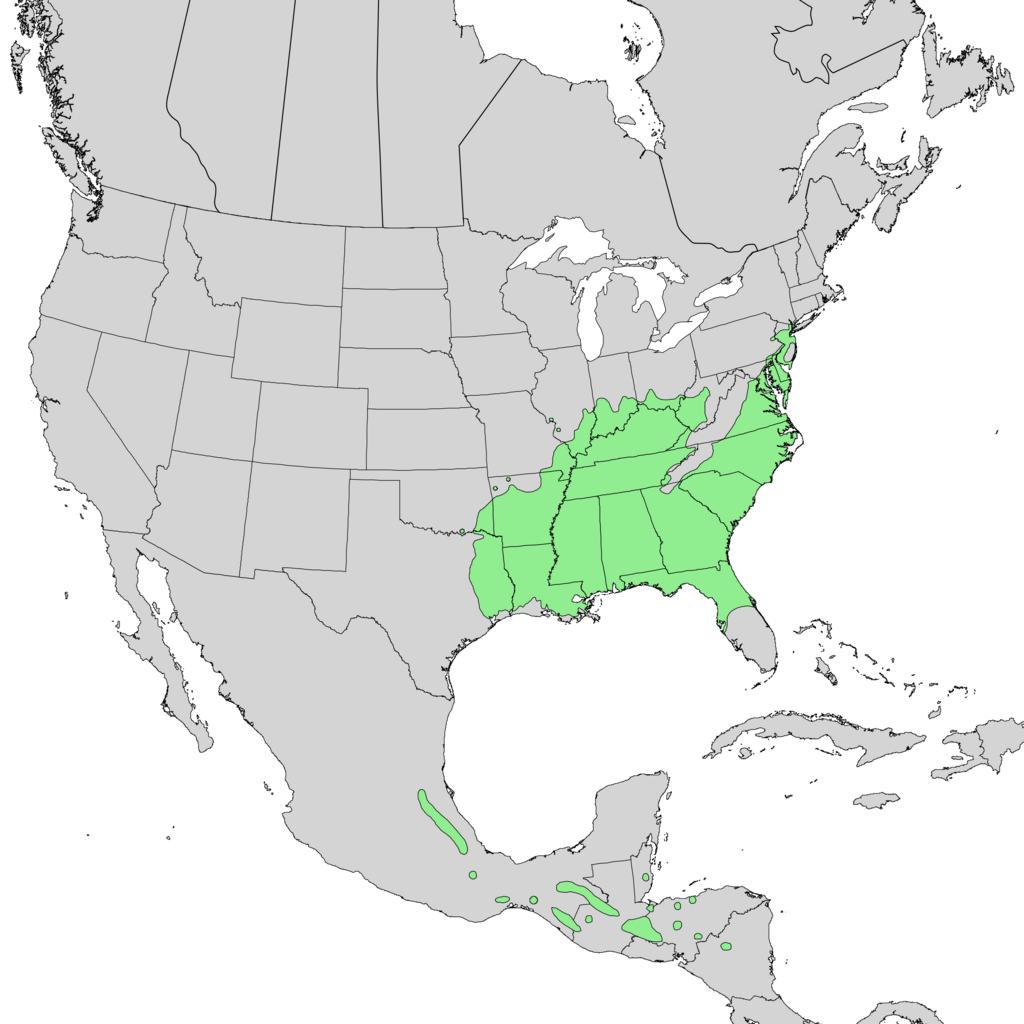
Native distribution of sweetgum. Wikimedia8
Wildlife Importance
It is the host plant for luna moth larvae. Numerous songbirds consume the seeds, in particular the American goldfinch4.
Economic Importance
Sweetgum is commercially one of the most important hardwood species of the Southeast². Its wood is used for furniture, cabinets, interior trim, and plywood².
Threats
Sweetgum is largely resistant to damage, but beavers will girdle the trees and fire may also damage them².
Interesting Facts
- The resinous gum produced from the bark was used to make chewing gum4 .
- Sweetgum was previously placed in the witch-hazel family (Hamamelidaceae).
- The Maryland champion sweetgum is in Upper Marlboro with a height of 102 ft and circumference of 209 inches (= 5.5 ft diameter) as measured in 20195.
References
- USDA-NRCS Plant Fact Sheet: Sweetgum
- USDA-Forest Service Silvics Vol. 2 Hardwoods: Liquidambar styraciflua
- CalPhotos: Liquidambar styraciflua leaves
- North Carolina State Extension: Liquidambar sturaciflua
- Maryland State Champion Trees
- CalPhotos–Liquidambar styraciflua
- Missouri Botanical Garden: Liquidambar styraciflua
- Maryland Biodiversity Project: Sweet gum
Contributed by J. Hull
* Imaged used with permission of photographer
