Blackjack Oak
Quercus marilandica Münchh.
Description
Blackjack oaks belong to the beech family (Fagaceae) ¹. Other common names include Jack oak, black oak and barren oak 5. They but can reach 100 feet tall 5, but typically grow up to 60 feet and are classified as a medium-sized tree ¹. Trunk diameter may reach 16 to 24 inches 6. Its trunk is almost black, with rough bark that is deeply furrowed with square or rectangular blocks ¹. Dead branches may persist for many years³. The leaves of blackjack oaks are leathery with three bell-shaped, bristle-tipped lobes ¹. Leaves are dark green on the upper surface and and yellowish on the lower surface with light brown hairs ¹. Some of its leaves can also last throughout the winter, a phenomenon called leaf marcescence 5,13. The trees are monoecious, as both male and female parts grow on the same tree 6. Female flowers are short spikes, and the males are yellow-green catkins. Its fruits area acorns, 0.5 to 1 inch long with a cap overing one-third to half its length ¹.
Bark of blackjack oak. @. A.Santillana. North Carolina State Extension 12.
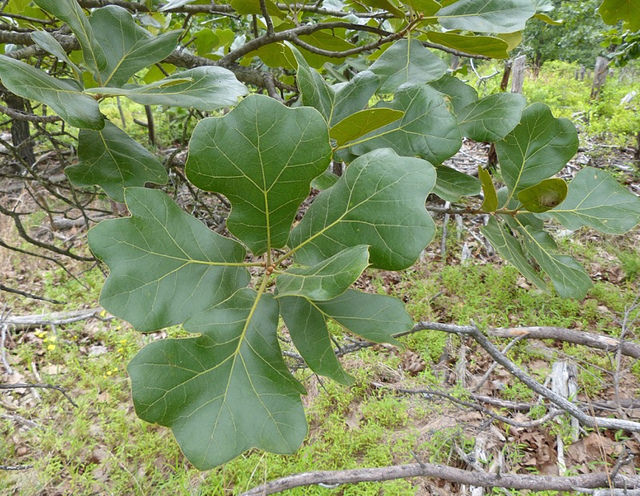

Blackjack oak leaves. @ J. Brighton, 2013. Maryland Biodiversity Project 7.

Acorn of blackjack oak. @ B. Kirchoff. North Carolina State Extension 12.
Distribution
Blackjack oaks are found in the Southeastern United States ² from New Jersey south to Georgia and northern Florida, west to Kansas and eastern Texas 9. Blackjack oak is usually found with drier soils. It is found in Texan savannas and prairie habitats 8. After fires, it is one of the first species to grow in the area. It can also withstand forest fires because of its thick bark, which makes it more common in forests more susceptible to fires 8. It is shade intolerant nor does it tolerate flooding 13. It grows on soils acidic soils with a pH range of 4.6 to 5.5 4. In Maryland it grows on the coastal plain and is frequent on serpentine barrens 7.
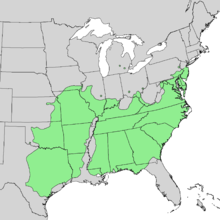
Native range of blackjack oak. Cross Timbers 13.
Wildlife Importance
The blackjack oak produces acorns which are important for squirrels and is also a nesting site for many birds, including woodpeckers. White M Hairstreak moth and Horace’s Duskywing use the tree as a larval host ³. Many mammals also use its acorns as a food source, including snakes, deer, and raccoons ³.
Economic Importance
Due to the nature of the blackjack oak from size to growth rate, it has limited economic uses for humans and therefore limited economic importance. This tree is specifically known for being gangly and extremely hard wood 8,11. Blackjack oak wood is used for railroad ties and fenceposts ³. It has also been used for fuel and charcoal ¹. Individuals also use the tree for firewood and building materials 6.
Threats
Many diseases can infect the blackjack oak, including ones that affect many different types of oak, including Oak Leaf Blister, Oak Tatters, and Oak Wilt. Insects can also attack the trees and will consume its foliage and sap inside branches, taking essential nutrients 5. Fungi can also overtake the tree, including the canker fungus and two lined chestnut borer can kill blackjack oak trees. Many taller species can outcompete it 10.
Interesting Facts
- The blackjack oak is known for its tolerance to drought and fire which is higher than most oaks 13.
- The Choctaw, a Native American tribe in the Southeastern United States, use blackjack oak for pain relief during birth ³.
- The blackjack oak is unique in that it is one of the few trees to grow in very dry soils and can even grow in gravel and limestone 6.
- The oldest specimen found was 230 years old in Oklahoma 8.
- The blackjack oak was first named after discovery in Maryland which is reflected in its latin species name which means “of Maryland” 11. The common name refers to the club-shaped leaf that resembles a leather covered club 11.
References
- Missouri Department of Conservation: Blackjack oak
- USDA Plants: Quercus marilandica
- Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center: Quercus marilandica
- Dave’s Garden: Blackjack oak
- Iowa State University Extension and Outreach: Blackjack oak
- Texas A&M Forest Service: Blackjack oak
- Maryland Biodiversity Project: Blackjack oak
- USDA-Forest Service Fire Effects Information System: Quercus marilandica
- Flora of North America distribution map: Quercus marilandica
- Ohio Department of Natural Resources: Blackjack oak
- Chasing trees: Blackjack oak
- North Carolina State Extension: Quercus marilandica
- Cross Timbers: Blackjack Oak Tree

