Cherrybark Oak
Quercus pagoda Raf.
Description
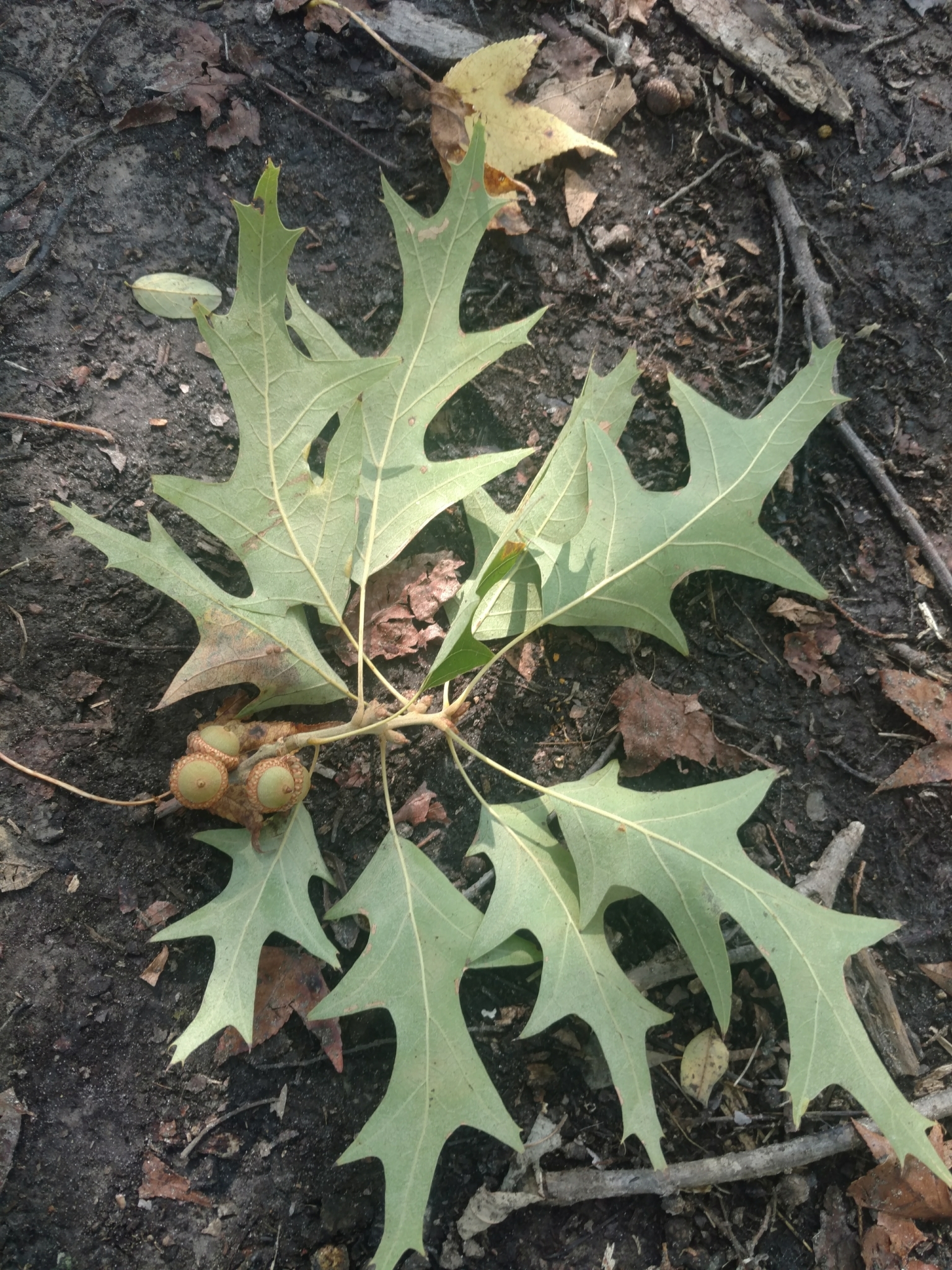
Cherrybark oak (family Fagaceae) is a large deciduous tree that can reach heights of 130 feet. ³ As the gray bark matures, it sometimes forms plates resembling that of black cherry, hence the common name. The leaves are alternate on the stem and have 5 to 11 lobes that are opposite and resemble a pagoda from which the scientific name comes. The leaves are 5 to 8 inches long and 3 to 5 inches wide.³ The lobes are bristle-tipped and are cut about one-half way to the midrib. ¹ The leaf base is wedge-shaped rather than rounded. 7 Showers are monoecious with male and female flowers on the same tree.¹ The acorns are 0.5 inch long with the upper one-third covered by the cap. ³
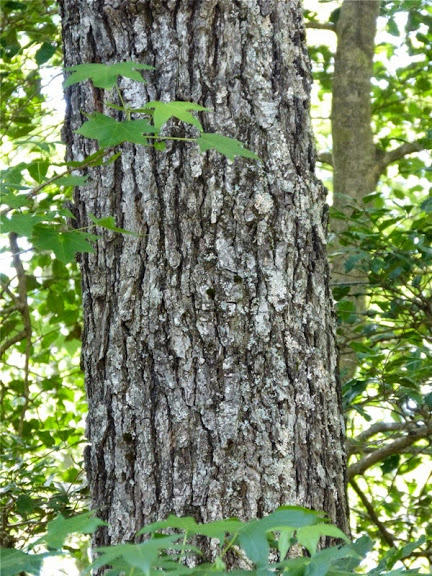

Bark of cherry bark oak. @ J. Brighton*, Maryland Plant Atlas. ²
Leaves and acorns of cherry bark oak. @ W. Longbottom (CC-BY-NC), Maryland Plant Atlas ²
Distribution
Cherrybark oak is found in the Southeastern US from Maryland to Florida and west to Texas and north up the Mississippi River valley to Illinois. ³ Found in bottomland forests, 5 it is largely confined to well drained soils. ¹ In Maryland cherrybark oak is distributed on the Coastal Plain of Southern Maryland and the Eastern Shore. ²
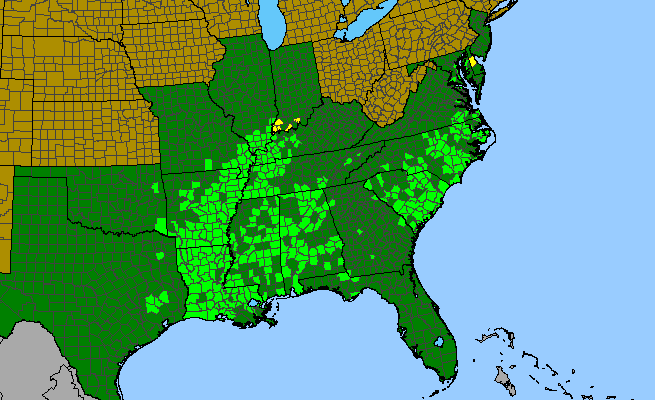
Distribution of cherry bark oak. Trees of North Georgia. 5
Wildlife Importance
Cherry bark oak acorns are consumed in quantity by numerous birds including wild turkey, blue jay, wood duck, red-bellied woodpecker and redheaded woodpecker. ¹ Additionally, several mammals such as deer, eastern fox squirrel and racoons consume the acorns. ¹ The leaves are host to several leafhoppers (Eratoneura app.), bugs, beetles and weavels, all ow which attract numerous insectivorous birds. 7 The tree is considered to have a high wildlife value. 7
Economic Importance
The wood of cherry bark oak is rated superior to the oaks of the southern United States and can be used for cabinets, furniture and veneer. 6 Because of its self-pruning growth habit , cherry bark oak grows relatively knot free, which increases its value. 7 It is fast growing compared to other oaks and is as an excellent landscape tree. 6
Threats
Cherrybark oaks are susceptible to wood-boring insects such as the carpenter worm and red oak borer. ¹ Like many oaks, cherry bark oak is affected by the oak wilt fungus (Ceratocystis fagacearum). ¹
Interesting Facts
- Cherrybark oak does not begin producing acorns until it is approximately 25 years old. ¹
- The largest cherry bark oak in Maryland is in Queen Anne’s County and is 109 feet tall and 75 inches in diameter. 4
References
- USDA NRCS Plant Guide: Cherrybark oak
- Maryland Plant Atlas: Quercus pagoda
- North Carolina Extension: Quercus pagoda
- Maryland Big Trees
- Guide to the Trees of North Georgia and Adjacent States: Quercus pagoda
- Missouri Department of Conservation: Cherrybark oak
- Illinois Wildflowers; Cherrybark oak
* Imaged used with permission of photographer.
Contributed by J. Hull

